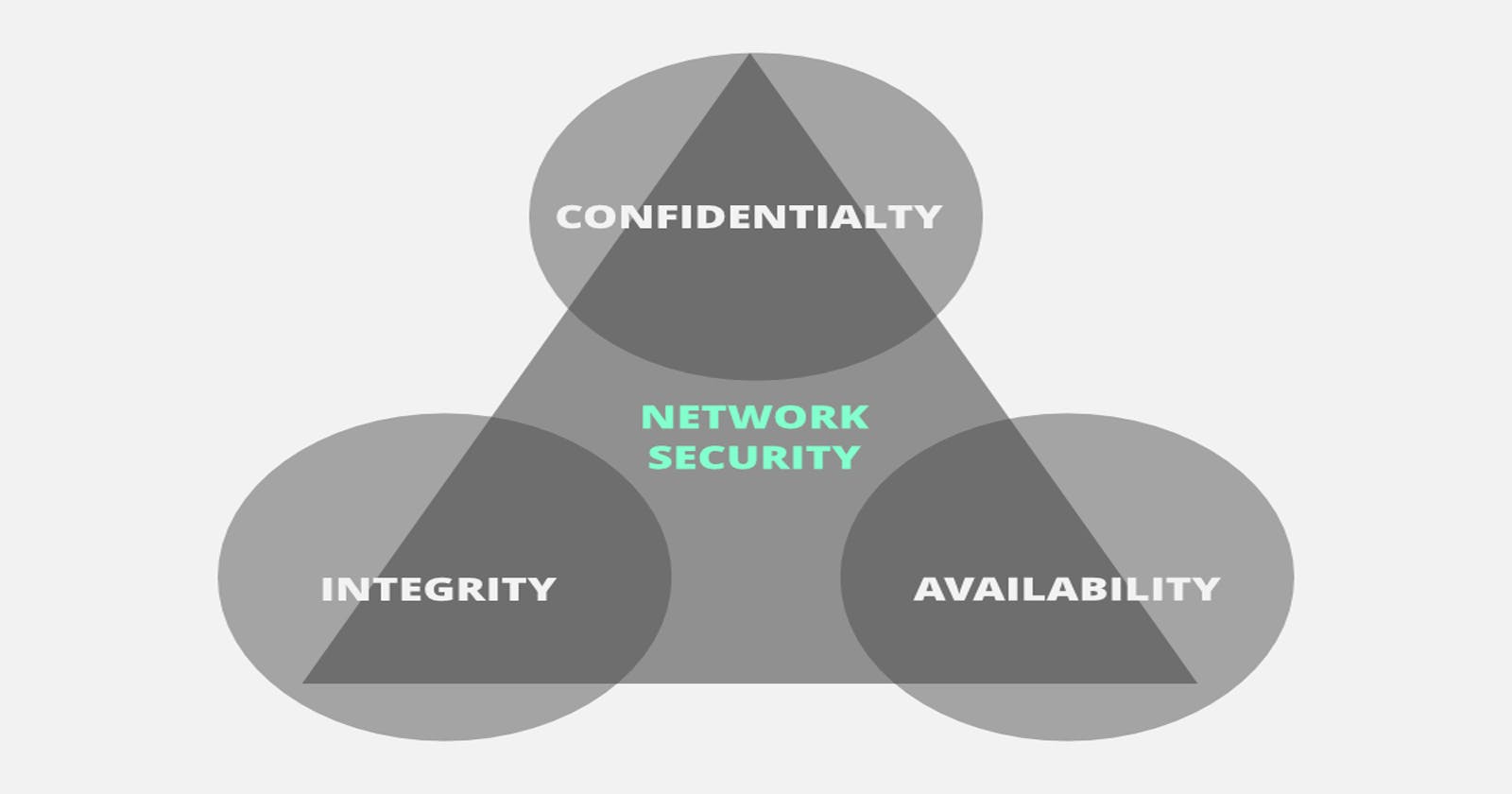
The CIA is an abbreviation for Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability. The CIA Triad is a standard model that forms the basis for security system development. This triad is especially important when working with defensive security since it helps you prioritize the risk based on the impact and how the impact correlates with the business.
This is especially important for organizations as this helps them to identify priority areas to invest in (and to provide more resources) to reduce the impact or damage to the company in the event of a cyber attack. For instance, an attack on the availability of the informational web page of an HR company may result in a minimal impact on the business, while an attack on the confidential information that they manage could be catastrophic. As a result, confidentiality is put first when it comes to these events.
We will now have a look at each component of the CIA Triad in detail to understand their basic concept
Confidentiality
Confidentiality involves the efforts of an organization to make sure data is kept secret or private. The attacks affecting confidentiality are based on access by an unauthorized person to the company's data. But how do you know who can access which kinds of data? The best way to respond to this question is by following the best practice that says that all
companies must have their data classified and labeled based on its sensitivity.
The data can be classified as follows:
• Restricted: This is the most important data the company possesses as it may include
trade secrets that, if disclosed, could have a catastrophic impact on the company.
• Confidential: This is data that companies must keep confidential (on a need to-
know basis). Many times, this type of data is associated with some external
regulations, and sanctions and fines may apply if disclosed.
• Private: This is less sensitive data. However, it is not intended for public
consumption and should be maintained within the organization.
• Public: This is data that is intended for public distribution (most of the time, it is
available and indexed online).
Integrity
Besides keeping the data confidential, we also need to ensure that data is not altered by a malicious actor. Integrity involves making sure your data is trustworthy and free from tampering. The integrity of your data is maintained only if the data is authentic, accurate, and reliable.
This is especially relevant if your company runs a transactional website (such as an e-commerce website) because an attacker may attack your database and create or modify discount codes and, by the time you discover the issue, your merchandise may already be sold and delivered for a fraction of the original price.
Therefore, due to the impact of these kinds of attacks, companies must proactively and constantly invest time and resources to prevent them.
Availability
Even if data is kept confidential and its integrity maintained, it is often useless unless it is available to those in the organization and the customers they serve. This means that systems, networks, and applications must be functioning as they should and when they should. Also, individuals with access to specific information must be able to consume it when they need to, and getting to the data should not take an inordinate amount of time.
These attacks aim to disrupt the availability of a given system, network, or web resource. Except for online stores, these are the less dangerous type of attack; however, such attacks are also the most common type of attack. In fact, the majority of the attacks performed by Hacktivist groups aim to disrupt system availability.